
UTC is one of several closely related successors to GMT. UTC does not observe daylight saving time.įor most purposes, UTC is considered interchangeable with GMT, but GMT is no longer precisely defined by the scientific community. UTC is, within about 1 second, mean solar time at 0°. In 1960, the International Radio Consultative Committee formalized the concept of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which became the new international civil time standard. time-zone system grew from this, in which all zones referred back to GMT on the prime meridian.
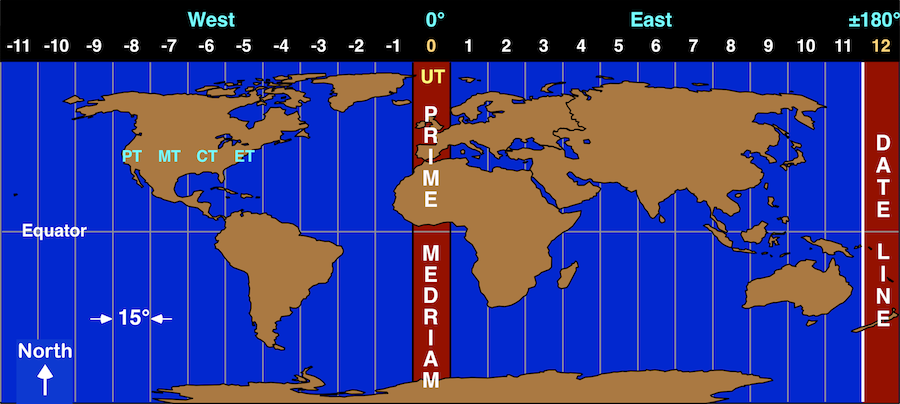
The conference therefore established the Greenwich Meridian as the prime meridian and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) as the world's time standard. In October 1884, the International Meridian Conference at Washington, D.C., decided that the prime meridian for longitude and timekeeping should be one that passes through the center of the transit instrument at the Greenwich Observatory in the United Kingdom. Four standard time zones for the continental United States were introduced at noon on November 18, 1883, in Chicago, IL, when the telegraph lines transmitted time signals to all major cities. Operators of the new railroad lines needed a new time plan that would offer a uniform train schedule for departures and arrivals. Weather service chief Cleveland Abbe introduced four standard time zones for his weather stations, an idea which he offered to the railroads.

Railroad managers tried to address the problem by establishing 100 railroad time zones, but this was only a partial solution to the problem. Time zones were therefore a compromise, relaxing the complex geographic dependence while still allowing local time to be approximate with mean solar time. Every city in the United States used a different time standard so there were more than 300 local sun times to choose from.
UTC TIME WIKIPEDIA DRIVERS
Train drivers must recalculate their own clocks in order to know departure time. Time calculation became a serious problem for people traveling by train (sometimes hundreds of miles in a day), according to the Library of Congress. Each train station set its own clock making it difficult to coordinate train schedules and confusing passengers. American railroads maintained many different time zones during the late 1800s. The use of local solar time became increasingly awkward as railways and telecommunications improved. Noon occurred at different times but time differences between distant locations were barely noticeable prior to the 19th century because of long travel times and the lack of long-distance instant communications prior to the development of the telegraph. See also: Standard time in the United Statesīefore the adoption of four standard time zones for the continental United States, many towns and cities set their clocks to noon when the sun passed their local meridian, pre-corrected for the equation of time on the date of observation, to form local mean solar time. It is the combination of the time zone and daylight saving rules, along with the timekeeping services, which determines the legal civil time for any U.S. The clocks run by these services are kept synchronized with each other as well as with those of other international timekeeping organizations. Official and highly precise timekeeping services (clocks) are provided by two federal agencies: the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (an agency of the Department of Commerce) and the United States Naval Observatory (USNO). The time zone boundaries and DST observance are regulated by the Department of Transportation, but no single map of those existed until the agency announced intentions to make one in September 2022. In the United States, time is divided into nine standard time zones covering the states, territories and other US possessions, with most of the country observing daylight saving time (DST) for approximately the spring, summer, and fall months.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
